Essential First Aid Tips Everyone Should Know
Essential First Aid Tips Everyone Should Know
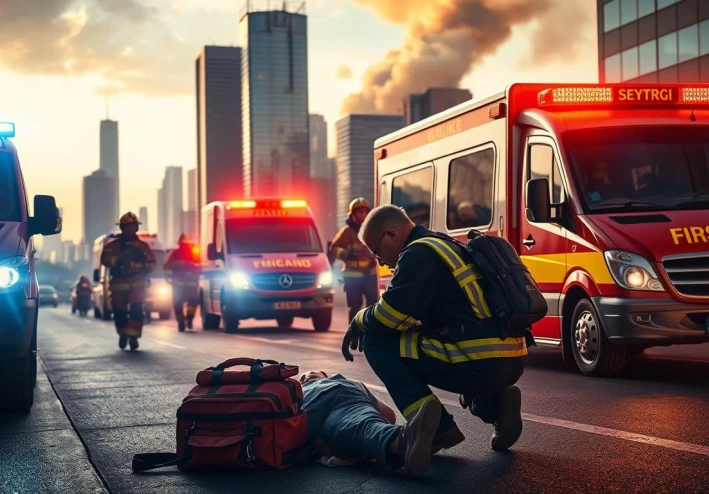
Can you imagine being in a situation where someone's life is in your hands? Knowing the right emergency response techniques can make all the difference. In a split second, you could be the difference between life and death.
Having basic knowledge of medical assistance skills is not only useful but also easy to learn. It can save someone's life or even your own. In this article, we will cover the essential tips that everyone should know to respond effectively in emergency situations.

For additional guidance, you can also visit our YouTube channel (https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCCgA72VEaCeISyW88zLbNUA) where we provide video content on first aid techniques.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the basics of emergency response.
- Learn essential first aid techniques.
- Know when to seek medical assistance.
- Be prepared for unexpected situations.
- Utilize additional resources for comprehensive learning.
The Life-Saving Value of First Aid Knowledge
Understanding the importance of first aid knowledge can be the difference between life and death in emergency situations. First aid is not just about treating minor injuries; it's about providing critical care that can save lives until professional medical help arrives.
The Critical Time Gap Between Injury and Professional Help
In many emergency situations, the time between an injury occurring and professional medical help arriving can be crucial. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), a form of basic life support, is a prime example where immediate action can significantly improve survival chances. CPR provides artificial ventilation that can preserve brain function, blood circulation, and breathing in a person.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4G67yN-7L2Y
Statistical Impact of Immediate First Aid Response
Statistics underscore the importance of immediate first aid. According to the American Heart Association, CPR performed by a bystander can double or triple a victim's chances of survival after cardiac arrest. Moreover, timely first aid can reduce the severity of injuries and prevent complications.
"For every minute that passes without CPR or defibrillation, the chance of survival from cardiac arrest decreases by 7% to 10%."
American Heart Association
Building Confidence to Act in Emergency Situations
Having first aid knowledge not only equips individuals with the skills to respond but also builds confidence to act in emergencies. First responder training programs are designed to prepare individuals for such situations, teaching them how to assess emergencies and provide appropriate care.
| First Aid Action | Impact |
|---|---|
| CPR | Improves survival chances after cardiac arrest |
| Immediate Bleeding Control | Reduces severity of injury |
| Proper Wound Care | Prevents infection and promotes healing |
By understanding the value of first aid and being prepared to act, individuals can make a significant difference in emergency situations.
Building and Maintaining Your First Aid Kit
Having a properly maintained first aid kit can make a significant difference in emergency situations. A first aid kit is not just a box of supplies; it's a critical tool for providing immediate care when injuries occur.
Essential Supplies for a Basic Home First Aid Kit
A basic home first aid kit should include a variety of supplies to treat common injuries. These include:
- Anti-bacterial wipes
- Painkillers
- Gauze pads
- Sunscreen
- Medical gloves
- Medical instrument kit
- Sling
- Burn gel
- Antibiotic ointment
- Antiseptic wipes
- First aid instructions
- Tourniquet
Specialized Kits for Travel, Outdoor Activities, and Vehicles
Depending on your activities and environment, you may need specialized first aid kits. For example, a travel kit might include medications for common travel ailments, while an outdoor kit might have supplies for treating snake bites or allergic reactions.
| Activity | Additional Supplies |
|---|---|
| Travel | Motion sickness medication, water purification tablets |
| Outdoor | Snake bite kit, blister care |
| Vehicle | Reflective triangles, emergency blanket |
Regular Maintenance and Replacement Schedule
Regularly checking and maintaining your first aid kit is crucial. This includes:
Checking Expiration Dates
Ensure that all medications and supplies are within their expiration dates.
Restocking Used Items
After using any item from your kit, restock it as soon as possible.

How to Assess Emergency Situations Quickly
The key to effective emergency response lies in the ability to assess the situation quickly and make informed decisions. In emergency situations, every second counts, and the actions taken can significantly impact the outcome.
Performing the Primary Survey: DRSABCD Protocol
The DRSABCD protocol is a systematic approach to assessing emergency situations. It stands for Danger, Response, Send for help, Airway, Breathing, Circulation, and Disability. This protocol helps first responders and individuals assess the situation, identify potential hazards, and provide appropriate medical assistance.
To apply the DRSABCD protocol, start by checking the scene for danger, then check the person's response, and send for help if necessary. Next, assess the airway, breathing, and circulation, and check for any disability.
Recognizing Life-Threatening Conditions
Recognizing life-threatening conditions is critical in emergency response. Conditions such as cardiac arrest, severe bleeding, and difficulty breathing require immediate attention. First responder training teaches individuals how to identify these conditions and respond appropriately.
When and How to Call 911 Effectively
Calling 911 is a crucial step in emergency response. When calling 911, it's essential to remain calm and provide clear information to the dispatcher.
Information to Provide to Dispatchers
When calling 911, provide the dispatcher with your location, the nature of the emergency, and the number of people involved. This information helps dispatchers send the appropriate response team.
Following Dispatcher Instructions
After calling 911, follow the dispatcher's instructions carefully. They are trained to provide guidance on how to respond to the emergency until help arrives.
| DRSABCD Step | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Danger | Check the scene for hazards | Ensure safety for yourself and the victim |
| Response | Check the person's response | Call for help if unresponsive |
| Send for help | Call 911 or send someone to get help | Provide clear information to the dispatcher |
Essential First Aid Techniques for Common Emergencies
In emergency situations, applying the correct first aid techniques can be the difference between life and death. First aid knowledge empowers individuals to respond effectively and confidently until professional medical help arrives.
Proper Hand Positioning and Body Mechanics
When administering first aid, proper hand positioning and body mechanics are crucial to prevent further injury to both the rescuer and the victim. For instance, when performing chest compressions during CPR, it's essential to position your hands correctly on the center of the chest and maintain straight arms to facilitate effective compressions.

Universal Precautions to Prevent Disease Transmission
Universal precautions are guidelines designed to prevent the transmission of diseases during first aid. These include wearing gloves, using barrier devices for rescue breathing, and properly disposing of contaminated materials. Adhering to these precautions minimizes the risk of infection for both parties involved.
Effective Communication During Emergency Response
Clear and effective communication is vital during emergency responses. This includes providing precise information to emergency services, communicating clearly with the victim if they are conscious, and coordinating with others present at the scene. Effective communication ensures a more streamlined and efficient response.
| First Aid Technique | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| CPR | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood circulation and oxygenation. | Critical for maintaining vital organ function until medical help arrives. |
| Wound Cleaning | Cleaning wounds with clean water and applying antibiotic ointment to prevent infection. | Reduces the risk of infection and promotes healing. |
| Use of EpiPen | Administering epinephrine via an EpiPen for severe allergic reactions. | Life-saving for individuals experiencing anaphylaxis. |
Recommended First Aid Resources from Our YouTube Channel
For visual learners, our YouTube channel offers a range of video tutorials on first aid techniques, including CPR, wound care, and using an EpiPen. These resources are designed to complement the information provided here and offer a practical guide to mastering first aid skills.
By learning and practicing these essential first aid techniques, individuals can significantly enhance their ability to respond to emergencies effectively. Regularly reviewing and updating first aid knowledge is crucial for staying prepared.
Mastering CPR and Choking Response
The ability to administer CPR and handle choking incidents effectively is a vital skill for everyone. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving technique that's useful in many emergencies, including heart attacks or near drowning, where someone's breathing or heartbeat has stopped.
Step-by-Step Adult, Child, and Infant CPR
CPR involves chest compressions and rescue breaths. The ratio of compressions to breaths varies among adults, children, and infants.
- Adult CPR: For adults, the American Heart Association recommends starting CPR with 30 chest compressions followed by two breaths.
- Child CPR: For children, after checking for unresponsiveness and not breathing, start CPR with 30 compressions or 15 compressions followed by two breaths if you're alone with the child.
- Infant CPR: For infants, CPR is slightly different; you use two fingers to compress the chest to about one-third of its depth.

How to Perform Hands-Only CPR for Bystanders
Hands-only CPR is recommended for bystanders who witness an adult suddenly collapse. It involves calling 911 and then pushing hard and fast on the center of the person's chest until help arrives.
- Call 911 or your local emergency number.
- Start compressions: Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, on the lower half of the breastbone. Place your other hand on top of the first hand.
- Push down on the chest at least 2 inches and at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute.
Executing the Heimlich Maneuver Correctly
The Heimlich maneuver is used to relieve choking on an object, such as food or other small items.
- Stand behind the person and wrap your arms around their waist.
- Make a fist with one hand, placing it just above the navel.
- Grasp your fist with your other hand and perform a quick upward thrust.
AED Usage: When and How to Apply
An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a portable device that checks the heart's rhythm and can send an electric shock, or defibrillation, to help the heart re-establish an effective rhythm.
| AED Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Turn on the AED | Follow the device's voice prompts or visual instructions. |
| 2. Prepare the chest | Remove any clothing or items from the chest as directed. |
| 3. Attach electrode pads | Place the pads on the bare chest as shown in the pictures on the pads. |
| 4. Analyze the heart rhythm | The AED will check the heart's rhythm and determine if a shock is needed. |
| 5. Deliver a shock (if advised) | Ensure no one is touching the person and press the button as instructed. |
Mastering these techniques can significantly enhance your ability to respond to emergencies effectively.
Treating Wounds and Traumatic Injuries
Effective treatment of wounds and traumatic injuries can significantly improve outcomes in emergency situations. Knowing the right techniques can make a substantial difference in the recovery process.
Controlling Severe Bleeding
To control severe bleeding, apply direct pressure to the wound using a clean cloth or bandage. Elevating the injured area above heart level can also help reduce blood flow.
It's crucial to maintain pressure until medical help arrives. If the bleeding is severe and doesn't stop, additional measures such as applying a tourniquet may be necessary, but this should be done with caution and ideally by someone trained in its use.
Burn Assessment and Treatment
Assessing the severity of a burn is critical. Burns are classified into three degrees: first-degree (affecting the outer layer of skin), second-degree (extending to the second layer), and third-degree (penetrating through all layers of skin).
For minor burns, cool the area with cool (not cold) water for 10-15 minutes. Cover the burn with a non-stick dressing. For severe burns, call 911 immediately and follow any instructions provided by the operator.

Immobilizing Sprains, Strains, and Suspected Fractures
For sprains and strains, apply the RICE principle: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This helps reduce pain and swelling.
For suspected fractures, immobilize the affected area using a splint if possible. Avoid moving the person unless they're in immediate danger.
Head Injury Management
Head injuries can be particularly dangerous. Monitor for signs of concussion or more severe injury, such as confusion, dizziness, or loss of consciousness.
If a head injury is suspected, keep the person calm and still. If they're wearing a helmet, do not remove it unless trained to do so.
| Injury Type | Immediate Care | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|
| Severe Bleeding | Apply direct pressure, elevate | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Burns | Cool with water, cover | Monitor for infection, seek medical help for severe burns |
| Sprains/Strains | RICE principle | Rest, physical therapy if necessary |
Responding to Serious Medical Emergencies
In life-threatening situations, knowing how to respond to serious medical emergencies can be the difference between life and death. These emergencies require immediate and appropriate actions to prevent further harm or even save a life.
Heart Attack and Stroke: FAST Recognition and Response
Recognizing the symptoms of heart attacks and strokes is crucial. The FAST acronym is a helpful tool:
- Face: Ask the person to smile. Does one side of their face droop?
- Arm: Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- Speech: Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence. Is their speech slurred or difficult to understand?
- Time: Time is of the essence. If the person shows any of these symptoms, call for emergency medical services immediately.
Safe Seizure Management Techniques
During a seizure, it's essential to keep the person safe. Clear the area around them of any hard or sharp objects, and gently turn them onto their side to help keep their airway clear. Do not restrain the person or put anything in their mouth.
Addressing Diabetic Emergencies: Hypoglycemia vs. Hyperglycemia
Diabetic emergencies can manifest as either hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Symptoms of hypoglycemia include shakiness, dizziness, and confusion. Hyperglycemia can cause increased thirst, dry mouth, and fruity-smelling breath. Providing the correct response, such as administering glucose for hypoglycemia, is critical.
Anaphylaxis Response and EpiPen Administration
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, and a drop in blood pressure. Administering an EpiPen involves injecting the medication into the middle of the outer thigh. Call emergency services immediately after using an EpiPen.
Being prepared to respond to these serious medical emergencies can significantly impact outcomes. Understanding the appropriate actions to take can help save lives and reduce the severity of the emergency.
Environmental Emergency First Aid Protocols
Effective first aid during environmental emergencies involves understanding the specific risks and responses required. Environmental emergencies can range from extreme temperatures to encounters with dangerous animals or plants.
Heat Exhaustion vs. Heat Stroke Treatment
Heat exhaustion and heat stroke are serious conditions that require immediate attention. Heat exhaustion is characterized by heavy sweating, pale skin, fast and weak pulse, nausea or vomiting, and dizziness. Heat stroke is more severe, with a body temperature of 103°F or higher, confusion, and dry, flushed skin with no sweating.
| Condition | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Exhaustion | Heavy sweating, pale skin, fast and weak pulse | Move to a cooler location, loosen clothing, and provide cool water |
| Heat Stroke | Body temperature of 103°F or higher, confusion, dry skin | Call 911, cool with ice or cold water, and fan the person |
Hypothermia and Frostbite Intervention
To treat hypothermia, be gentle with the afflicted person, move them out of the cold, remove wet clothing, and cover them with blankets. For frostbite, rewarm the affected area gradually with warm water, and avoid rubbing or massaging.
Near-Drowning Response and Water Safety
In cases of near-drowning, call 911 immediately, check for breathing and pulse, and begin CPR if necessary. Water safety measures include swimming with a buddy and knowing CPR.
Managing Animal Bites, Insect Stings, and Poisonous Plant Exposure
For animal bites, clean the wound with soap and water and seek medical attention. Insect stings can be treated by removing the stinger and applying a cold compress. Poisonous plant exposure requires washing the affected area with soap and water and removing contaminated clothing.
Conclusion: Preparing Yourself for Any Emergency
Having a knowledge of basic first aid skills could save someone's life or your own life. Being prepared for emergencies is crucial, and a well-stocked first aid kit is just the beginning.
The techniques and tips outlined in this article, from performing CPR to treating wounds and responding to serious medical emergencies, emphasize the importance of being equipped with the right skills. Understanding how to assess emergency situations quickly and effectively is also vital.
By mastering basic life support techniques and knowing how to use a first aid kit, you can make a significant difference in the outcome of an emergency. Staying informed and prepared is key to responding confidently in critical situations.
Take the first step today by reviewing your first aid kit and practicing the essential first aid techniques discussed in this article. Your actions could one day save a life.
FAQ
What is the most important thing to do in a medical emergency?
The most important thing to do in a medical emergency is to remain calm and call 911 or your local emergency number immediately. This ensures that professional help is on the way as soon as possible.
What are the essential items to include in a first aid kit?
Essential items to include in a first aid kit are bandages, antiseptic wipes, pain relievers, any medications that family members may need, and a first aid guide. It's also a good idea to include specialized items based on your specific needs, such as snake bite kits or epi-pens.
How do I perform CPR on an adult?
To perform CPR on an adult, start by calling 911. Then, begin chest compressions by placing the heel of one hand on the center of the chest and the other hand on top, pushing down 2 inches at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. After 30 compressions, give two breaths by tilting the head back, pinching the nose shut, and giving breaths that make the chest rise.
What is the DRSABCD protocol used for?
The DRSABCD protocol is used to assess emergency situations quickly. It stands for Danger, Response, Send for help, Airway, Breathing, Circulation, and Disability, and is a systematic approach to evaluating the severity of an emergency and determining the best course of action.
How do I treat a severe burn?
To treat a severe burn, cool the burn with cool (not cold) water for 10-15 minutes, then cover it with a non-stick, sterile dressing. Do not apply ice, butter, or any topical ointments. Seek medical attention immediately for severe burns, especially if they cover a large area or are on the face, hands, or feet.
What is the correct way to use an EpiPen?
To use an EpiPen, pull the safety cap off, place the tip against the middle of the outer thigh, and push down until you hear a click. Hold in place for a few seconds, then remove and massage the area. Call 911 immediately after using an EpiPen, as it is only a temporary measure to help alleviate severe allergic reaction symptoms.
How can I prevent disease transmission when providing first aid?
To prevent disease transmission when providing first aid, use universal precautions such as wearing gloves, using a barrier device for CPR, and washing your hands thoroughly after providing care. Avoid touching your face or other surfaces that may be contaminated.
What are the signs and symptoms of a heart attack?
The signs and symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, fatigue, and pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach. If you suspect someone is having a heart attack, call 911 immediately.
How do I respond to a seizure?
To respond to a seizure, keep the person safe by clearing the area around them of any objects that could cause injury. Turn them onto their side to help keep their airway clear, and loosen any tight clothing. Do not restrain them or put anything in their mouth. After the seizure, provide comfort and reassurance until they are fully recovered.