Skin Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Skin Conditions
Skin Diseases
Description:
Understanding skin diseases? This comprehensive guide explores various skin conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Learn about common concerns like acne, eczema, psoriasis, and more. Find helpful tips for maintaining healthy skin and preventing skin problems.
table of contents;
* Introduction: The Vital Role of Skin and Common Skin Concerns
* Types of Skin Diseases: Exploring a Spectrum of Conditions
* Inflammatory Skin Diseases: When the Skin Becomes Red and Irritated
* Infectious Skin Diseases: Caused by Viruses, Bacteria, or Fungi
* Genetic Skin Diseases: Inherited Conditions Affecting Skin Health
* Autoimmune Skin Diseases: The Body's Immune System Attacks Skin Cells
* Skin Cancers: Recognizing and Early Detection is Crucial
* Common Skin Diseases: In-Depth Look at Frequent Concerns
Acne: Understanding Pimples, Blackheads, and Whiteheads
* Eczema: Dry, Itchy Skin Affecting People of All Ages
* Psoriasis: A Chronic Skin Condition Causing Scaly Patches
* Rosacea: Facial Redness, Bumps, and Visible Blood Vessels
* Athlete's Foot and Fungal Nail Infections: Common Conditions in Moist Environments
* Warts: Noncancerous Skin Growths Caused by HPV
* Moles and Melanoma: Recognizing the Signs of Skin Cancer
* Maintaining Healthy Skin: Preventive Measures and Daily Practices
* Sun Protection: The Essential Step for Preventing Skin Damage
* Gentle Skincare Routine: Cleansing, Moisturizing, and Avoiding Harsh Products
* Managing Stress: The Impact of Stress on Skin Health
* Healthy Diet and Hydration: Nourishing Your Skin from Within
* Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
* When to See a Dermatologist: Seeking Professional Help for Skin Concerns
* Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Skin Health for a Radiant You
Introduction: The Vital Role of Skin and Common Skin Concerns
The skin is our largest organ, acting as a protective barrier against the external environment. It plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature, preventing water loss, and protecting us from harmful pathogens. However, various factors can disrupt skin health, leading to a wide range of skin diseases.
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of skin conditions. We'll explore different types of skin diseases, their causes, and treatment options. We'll also discuss some of the most common skin concerns, providing valuable information for recognizing and managing them.
Types of Skin Diseases: Exploring a Spectrum of Conditions
Skin diseases manifest in various ways, with different causes and treatment approaches. Here's a breakdown of some major categories:
Inflammatory Skin Diseases: When the Skin Becomes Red and Irritated
Eczema: A chronic inflammatory skin condition causing dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Psoriasis: An autoimmune condition leading to red, scaly patches on the skin.
Rosacea: A chronic inflammatory skin condition affecting the face, often characterized by redness, bumps, and visible blood vessels.
Seborrheic dermatitis: A common condition causing flaky, red, and itchy patches on the scalp, face, and upper body.
Infectious Skin Diseases: Caused by Viruses, Bacteria, or Fungi
Impetigo: A highly contagious bacterial skin infection causing red, crusty sores.
Cellulitis: A bacterial infection affecting deeper layers of the skin, causing redness, swelling, and pain.
Shingles: A viral infection causing a painful rash with blisters, typically following a previous chickenpox infection.
Athlete's foot and fungal nail infections: Fungal infections affecting the feet and toenails, causing itching, scaling, and discomfort.
Genetic Skin Diseases: Inherited Conditions Affecting Skin Health
Eczema: Certain types of eczema can have a genetic predisposition.
Psoriasis: Genetic factors play a role in the development of psoriasis.
Acne: A genetic component can influence
Acne: A genetic component can influence acne susceptibility. While not directly inherited, genes can determine how your skin reacts to hormones and bacteria, impacting acne development. Ichthyosis: A group of inherited skin conditions causing dry, scaly, and thickened skin. Neurofibromatosis: A genetic condition causing the growth of tumors on or under the skin and nerves.
Autoimmune Skin Diseases: The Body's Immune System Attacks Skin Cells
Psoriasis: In psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to inflammation and rapid skin cell growth.
Lupus: An autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs, including the skin, causing rashes, redness, and other skin problems.
Dermatitis herpetiformis: An autoimmune condition causing itchy, blistering eruptions on the skin, often associated with celiac disease.
Skin Cancers: Recognizing and Early Detection is Crucial
Basal cell carcinoma: The most common type of skin cancer, typically appearing as a pearly or waxy bump or a flat, scaly patch.
Squamous cell carcinoma: Another common skin cancer, often presenting as a red, scaly patch that may bleed.
Melanoma: The most serious type of skin cancer, appearing as an irregular mole with multiple colors and uneven borders. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
Actinic keratosis: Precancerous growths that may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated. They appear as rough, scaly patches on sun-exposed skin.
Common Skin Diseases: In-Depth Look at Frequent Concerns
Now that we've explored different types of skin diseases, let's delve deeper into some of the most common concerns people face:
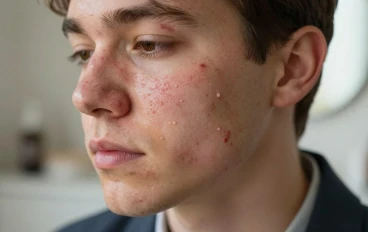
Acne: Understanding Pimples, Blackheads, and Whiteheads
Acne is a common skin condition affecting people of all ages, but most prevalent in teenagers and young adults. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, creating an environment for bacteria to grow. This leads to the development of pimples, blackheads (open clogged pores), and whiteheads (closed clogged pores).
Causes of Acne:
Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones during puberty, pregnancy, and menstruation can trigger acne breakouts.
Genetics: A family history of acne increases your risk.
Certain medications: Some medications can worsen acne.
Diet: While not a direct cause, a diet high in processed foods and sugary drinks may contribute to acne development.
Stress: Stress can exacerbate existing acne.
Treatment Options for Acne:
Over-the-counter (OTC) topical medications: These often contain benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or alpha hydroxy acids to combat bacteria and promote exfoliation.
Prescription medications: Depending on the severity, stronger topical medications or oral antibiotics may be prescribed by a dermatologist.
Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and practicing good skincare hygiene can significantly improve acne.
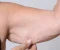
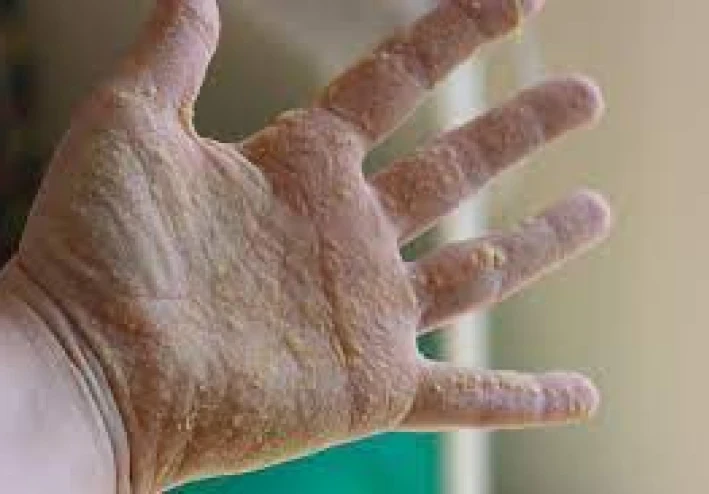
Eczema: Dry, Itchy Skin Affecting People of All Ages
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition causing dry, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. It can affect people of all ages, but often starts in childhood. There are different types of eczema, each with slightly varying triggers and symptoms.
Common Types of Eczema:
- Atopic dermatitis: The most common type of eczema, often triggered by allergens or irritants.
- Contact dermatitis: Caused by direct contact with an irritant or allergen.
- Hand eczema: Specifically affects the hands, causing dryness, cracking, and irritation.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Affects the scalp and oily areas of the face, causing redness, flaking, and itching.
Treatment Options for Eczema:
Moisturizers: Regular use of fragrance-free moisturizers helps hydrate
- Moisturizers: Regular use of fragrance-free moisturizers helps hydrate the skin and reduce itching.
- Steroid creams: Topical corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and itching. However, long-term use should be monitored by a doctor.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: These topical medications suppress the immune system's activity, reducing inflammation.
- Immunosuppressant medications: In severe cases, oral or injectable immunosuppressant medications may be prescribed.
- Identifying and avoiding triggers: Avoiding known triggers like allergens, irritants, and harsh soaps can significantly improve eczema symptoms.
Psoriasis: A Chronic Skin Condition Causing Scaly Patches
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes red, scaly patches on the skin. It can affect any part of the body, but commonly appears on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. While not contagious, psoriasis can be a lifelong condition with periods of flare-ups and remission.
Causes of Psoriasis:
- Genetics: Psoriasis has a strong genetic link.
- Immune system dysfunction: In psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid skin cell growth and the formation of plaques.
- Environmental triggers: Stress, infections, certain medications, and heavy alcohol consumption can trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis:
- Topical medications: These may include corticosteroids, retinoids, or calcineurin inhibitors to reduce inflammation and scaling.
- Light therapy: Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy can slow skin cell growth and improve symptoms.
- Oral medications: For moderate to severe psoriasis, oral medications that target the immune system or cell growth may be prescribed.
- Biologic drugs: These injectable medications target specific parts of the immune system involved in psoriasis.
Rosacea: Facial Redness, Bumps, and Visible Blood Vessels
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition affecting the face. It causes redness, visible blood vessels, small, pus-filled bumps, and occasionally, eye irritation. Although the exact cause is unknown, rosacea is thought to be linked to genetics, blood vessel abnormalities, and triggers like sun exposure, spicy foods, and alcohol.
Symptoms of Rosacea:
- Facial redness and flushing
- Visible blood vessels on the face (telangiectasia)
- Small, red, pus-filled bumps (papules and pustules)
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Enlarged pores
- Eye irritation (ocular rosacea)
Treatment Options for Rosacea:
- Identifying and avoiding triggers: Avoiding known triggers is crucial for managing rosacea.
- Topical medications: These may include metronidazole cream, ivermectin cream, or azelaic acid cream to reduce inflammation and redness.
- Oral antibiotics: In some cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to combat inflammation.
- Laser treatment: Laser therapy can help reduce the appearance of visible blood vessels.
Maintaining Healthy Skin: Preventive Measures and Daily Practices
While some skin conditions have a genetic predisposition, there are steps you can take to promote healthy skin and prevent common problems. Here are some key practices:
Sun Protection: The Essential Step for Preventing Skin Damage
Sun exposure is a major contributor to premature aging, wrinkles, and skin cancer. Here's how to protect your skin from the sun:
Seek shade: Avoid the sun during peak hours (10 am to 4 pm) whenever possible.
Wear protective clothing: Cover up with long sleeves, pants, and wide-brimmed hats. Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
Gentle Skincare Routine: Cleansing, Moisturizing, and Avoiding Harsh Products
A gentle skincare routine is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. Here's what to include:
Cleansing: Wash your face twice daily with a gentle cleanser suitable for your skin type. Avoid harsh soaps that can strip away natural oils.
Moisturizing: Use a moisturizer appropriate for your skin type to hydrate and protect the skin barrier.
Avoid harsh products: Skip
Avoid harsh products: Skip scrubs, abrasive cleansers, and excessive washing, which can irritate the skin.
Don't forget other areas: Moisturize dry areas like elbows, knees, and hands regularly.
Managing Stress: The Impact of Stress on Skin Health
Chronic stress can manifest on your skin in various ways, worsening acne, eczema, and rosacea. Here are some tips for managing stress and promoting healthy skin:
Relaxation techniques: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to manage stress effectively.
Getting enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Sleep deprivation can contribute to skin problems.
Healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains nourishes your skin from within.
Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity helps manage stress and improves overall well-being, positively impacting your skin.
Healthy Diet and Hydration: Nourishing Your Skin from Within
What you eat and drink can significantly affect your skin health. Here's how to nourish your skin from within:
Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and keep your skin plump.
Eat a balanced diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support skin health.
Healthy fats: Include healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil in your diet. Healthy fats are crucial for maintaining the skin barrier and promoting cell function.
Limit processed foods and sugary drinks: Excessive consumption of processed foods and sugary drinks can contribute to inflammation and worsen skin problems.
Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can damage your skin and accelerate aging. Smoking narrows blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the skin, leading to a dull and unhealthy appearance. Alcohol dehydrates the skin and can worsen inflammatory skin conditions.
When to See a Dermatologist: Seeking Professional Help for Skin Concerns
If you're concerned about a skin condition, experiencing persistent symptoms, or self-care measures aren't providing relief, consult a dermatologist. A dermatologist is a doctor specializing in skin, hair, and nail conditions. They can diagnose your skin condition, recommend the most appropriate treatment plan, and provide ongoing care.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Skin Health for a Radiant You
Skin is our body's largest organ, playing a vital role in protecting us from the external environment. By understanding different skin diseases, their causes, and preventive measures, you can take charge of your skin health. Implementing the practices discussed in this guide can help you achieve healthy, radiant skin and address any concerns effectively. Remember, early detection and treatment are crucial for managing skin conditions. If you notice any changes in your skin, don't hesitate to consult a dermatologist for professional guidance.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Always consult with your doctor before starting a new skincare routine or making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.