🫁 pothyroidism Uncovered: Symptoms, Causes, and What You Need to Know
🫁 pothyroidism Uncovered: Symptoms, Causes, and What You Need to Know


Introduction
Hypothyroidism — commonly known as an underactive thyroid — is a medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide, yet many don’t recognize the signs until the condition becomes more advanced. The thyroid gland plays a critical role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, body temperature, and more. When it fails to produce enough hormone, the body’s functions slow down, often leading to a variety of health issues.
In this article, we will explore what hypothyroidism is, common and less common symptoms, underlying causes, and why early diagnosis matters. We’ll also link to trusted health sources for deeper reading.
Brief Overview
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough thyroid hormone — primarily thyroxine (T4) — that the body needs to regulate metabolism and maintain vital functions. This condition can develop slowly over time and affect multiple organs and systems. Women and older adults are statistically more at risk.
Despite being common, hypothyroidism is often underdiagnosed because symptoms can be subtle or mistaken for aging, stress, or other health issues.
What is Hypothyroidism?
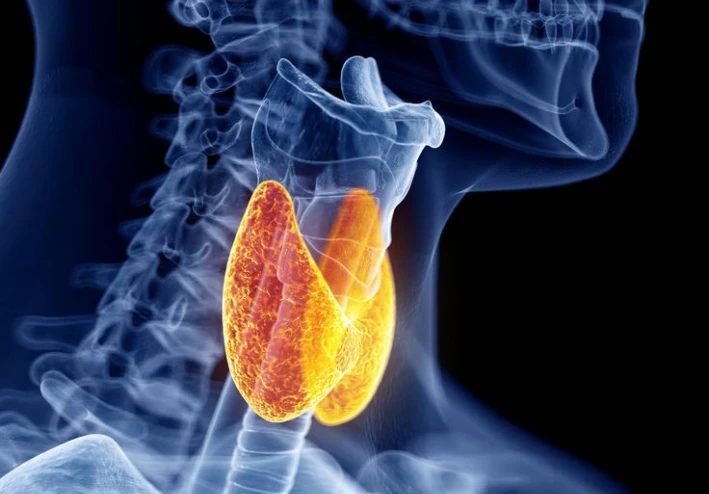
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. Its main role is to produce hormones that regulate metabolism — the chemical processes in the body that convert food into energy. When thyroid hormone levels fall below what the body needs, the result is hypothyroidism.
The condition slows the body’s normal biological processes, often causing fatigue, weight gain, mood changes, and other symptoms as organ systems react to the lack of hormone influence.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Symptoms usually develop gradually and vary significantly between individuals. Some people experience clear and strong signs early on, while others may have mild or nonspecific symptoms for years.
🔹 Common Symptoms
Most people with hypothyroidism experience:
- Persistent fatigue and low energy
- Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Increased sensitivity to cold
- Dry skin and hair, hair loss
- Slow heart rate
- Constipation
- Depression and mood swings
- Irregular menstrual periods or heavy flow
- Trouble concentrating or “brain fog”
🔹 Less Common Signs
Although less talked about, the following signs can also be associated with hypothyroidism:
- Puffiness in the face
- Hoarse voice
- Muscle weakness or joint pain
- Elevated “bad” cholesterol levels
- Swelling of the thyroid gland (goiter)
- Slower speech
- Cold intolerance even in mild temperatures
🧒 Symptoms in Children & Infants
In younger populations, hypothyroidism may manifest as:
- Growth delays
- Delayed puberty
- Slow mental development
- Slowed development of permanent teeth
- In infants: hoarse cry, lethargy, jaundice or poor feeding
Because symptoms can overlap with other conditions, medical testing is usually required to confirm a suspected diagnosis.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism has a range of causes, from autoimmune conditions to surgery or nutrient deficiencies. Here are the most common ones:
🧠 Autoimmune Disease (Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis)
This is the most prevalent cause of hypothyroidism in developed countries. The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, impairing hormone production.
📍 Thyroiditis
Inflammation of the thyroid gland due to infection, pregnancy (postpartum thyroiditis), or other causes can initially release stored hormones and later reduce thyroid function.
✂️ Surgery and Radiation
Surgical removal of the thyroid or radiation therapy to the neck/chest (often for cancer treatment) can damage or eliminate hormone-producing tissue.
💊 Medications
Certain drugs, including lithium, amiodarone, and some chemotherapy agents, can affect thyroid hormone production.
🧬 Congenital Conditions
Some infants are born with a poorly developed or absent thyroid gland — a condition known as congenital hypothyroidism. Early screening and treatment prevent serious developmental issues.
🧠 Pituitary Gland Disorders
Rarely, hypothyroidism results from insufficient stimulation of the thyroid due to a pituitary gland disorder.
🧂 Iodine Imbalance
Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. Too little (or sometimes too much) iodine in the diet can affect hormone synthesis — more common in areas without iodized food.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing hypothyroidism:
- Female sex
- Family history of thyroid disease
- Being over age 60
- Autoimmune conditions like type 1 diabetes or celiac disease
- History of thyroid surgery or radiation
- Pregnancy and the postpartum period
Recognizing these risk factors helps both patients and clinicians monitor thyroid health more proactively.
Why Hypothyroidism Matters
If left untreated, hypothyroidism can worsen and contribute to other health issues:
- Heart problems: Low thyroid hormone can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Infertility & pregnancy complications: Hormone imbalance can disrupt ovulation, causing fertility issues and pregnancy risks like pre-eclampsia or miscarriage.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Nerve damage causing numbness or pain in limbs over time.
- Myxedema coma: A rare, life-threatening condition characterized by extreme cold intolerance and unconsciousness — a medical emergency.
Diagnosis & Treatment (Short Overview)
Diagnosis is typically confirmed through blood tests measuring:
- TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)
- Free T4 levels
An elevated TSH and low T4 are classic signs of hypothyroidism.
Treatment generally consists of daily hormone replacement therapy — most often levothyroxine — which restores normal hormone levels and eases symptoms. Once a proper dose is found, treatment is usually lifelong but highly effective.
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism is a common but often overlooked medical condition that can significantly affect quality of life if undiagnosed or untreated. With symptoms ranging from fatigue and weight gain to mood disturbances and cold intolerance, it can mimic many other health issues. Early awareness, reliable testing, and consistent medical care allow most people with hypothyroidism to live healthy, symptom-free lives.
If you suspect you or a loved one may be experiencing symptoms of an underactive thyroid, consult a healthcare professional and refer to reliable sources like the Mayo Clinic and NHS guidelines linked above.
Useful Links
✅ Mayo Clinic – Hypothyroidism Symptoms & Causes: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hypothyroidism/symptoms-causes/syc-20350284
✅ NHS – Underactive Thyroid Guide: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/underactive-thyroid-hypothyroidism/
✅ Cleveland Clinic – Hypothyroidism Overview: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12120-hypothyroidism