What is canine disease and how do you protect yourself from it?
Rabies: symptoms and treatment
Rabies, also known as epidemic rabies, is a serious condition caused by a viral infection that affects the nervous systems of humans and animals. The virus is usually transmitted from the bite of an infected animal, especially dogs, to humans. Prompt prevention and medical intervention are essential to reduce the severity of the disease.
Symptoms of rabies:
Symptoms of rabies usually develop in stages, with the first stage including non-specific symptoms similar to common illnesses such as fever, fatigue, and headache. Symptoms become more severe over time and include:
Behavioral and neurological changes: such as anxiety, aggression or isolation.
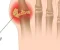
Severe pain at the bitten site.
Muscle cramps and spasms.
General weakness leading to difficulty swallowing and breathing.
Treatment of rabies:
Effective treatment of rabies requires immediate medical intervention. Treatment is given with an antiviral serum as soon as symptoms appear. Although there is no proven cure for advanced rabies, it can be prevented with anti-rabies vaccine doses.
Prevention and warning:
If you think you are at risk from rabies, you should seek immediate medical care. Prevention and early intervention can be crucial in treating this serious disease.
Cleaning the wound:
Wash the wound well with soap and water for 15-20 minutes to reduce transmission of the virus.
Start vaccination immediately:
Prompt treatment and rapid response require starting an anti-rabies vaccination schedule. This schedule consists of rabies vaccine doses given over a certain period.
Biological treatment (anti-rabies serum):
Giving a dose of anti-rabies serum known as Immunoglobulin G (IG) to the wound site can help prevent the spread of the virus and limit infection.
Dog vaccine doses:
Start an immediate anti-rabies vaccination schedule according to the approved medical protocol.
Medical follow-up:
It is necessary to follow up on the condition with the treating physician to ensure that the necessary doses of vaccines are given on time and to check the body's response to treatment.
Supportive care:
Doctors can sometimes use supportive treatments to relieve infection-related symptoms and maintain overall health.
Prevention in the future:
After recovery, the person must adhere to the dog's full vaccination schedule to maintain prevention against any future infection.
Remember, early and effective treatment can be crucial in reducing the risk of rabies. It is essential to seek immediate medical care if you are bitten by an animal suspected of carrying the virus.
التطعيم: يجب تطعيم الحيوانات المنزلية مثل الكلاب بانتظام لمنع الإصابة بداء الكلب. @تجنب الاتصال الوثيق مع الحيوانات غير المعروفة أو المشتبه فيها. @اطلب الرعاية الطبية الفورية في حالة حدوث عضة أو اتصال بحيوان يشتبه في إصابته بالكلاب. @خاتمة: