Pneumonia
Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
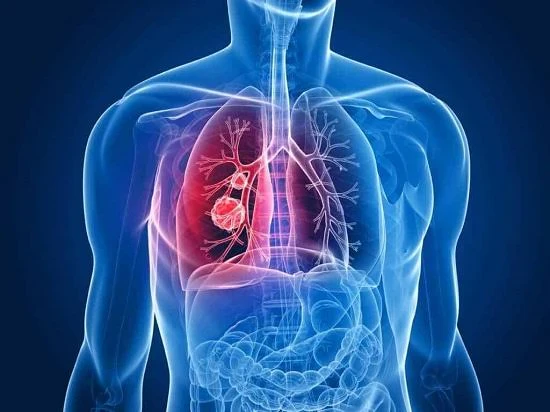
Pneumonia is a common disease that affects the respiratory system and can pose a serious health risk if not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner. This condition occurs as a result of inflammation of the air sacs in one or both lungs, which become filled with fluid or pus. As a result, breathing becomes difficult and the lungs’ ability to supply the body with oxygen is reduced.
Causes of Pneumonia
The causes of pneumonia vary, with infection being the most common cause. These include:
Bacterial infections, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is the most common cause among adults.
Viral infections, such as influenza viruses or the coronavirus.
Fungal infections, which usually occur in individuals with weakened immune systems.
The risk of developing pneumonia increases among the elderly, children, smokers, and individuals with chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Symptoms of pneumonia differ from one person to another depending on age and general health condition. However, the most common symptoms include:
Persistent cough accompanied by mucus
High fever and chills
Shortness of breath and chest pain
Severe fatigue and general weakness
Rapid heartbeat
In severe cases, confusion may occur, especially among elderly patients. These symptoms should not be ignored, as delayed treatment may lead to serious complications.
Diagnosis of Pneumonia
The diagnosis of pneumonia depends on a clinical examination of the patient, in addition to several tests such as chest X-rays, blood tests, and sputum analysis to determine the type of infection. This helps the physician choose the most appropriate treatment.
Treatment of Pneumonia
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the infection:
In cases of bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are used.
Viral pneumonia is usually treated with antiviral medications, along with rest and adequate fluid intake.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to provide oxygen therapy or intravenous fluids.
Following the doctor’s instructions and completing the full course of treatment is essential to ensure full recovery.
Prevention of Pneumonia
The risk of pneumonia can be reduced by following several preventive measures, such as:
Receiving necessary vaccinations, especially the influenza vaccine and the pneumococcal vaccine
Washing hands regularly
Quitting smoking
Strengthening the immune system through healthy nutrition
Avoiding contact with individuals suffering from respiratory infections
Complications of Pneumonia
If pneumonia is not properly treated, it may lead to serious complications, particularly among elderly individuals and those with weakened immune systems. The most significant complications include:
Respiratory failure requiring the use of mechanical ventilation
Sepsis, which is a medical emergency
Accumulation of fluid around the lungs
Formation of lung abscesses in some severe bacterial cases
Therefore, early medical intervention plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of these complications.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Medical attention should be sought immediately if severe symptoms appear, such as:
Significant difficulty breathing
Persistent high fever that does not respond to medication
Severe chest pain
Bluish discoloration of the lips or extremities
Deterioration of general condition or mental confusion
Relying solely on home remedies is not recommended, especially for children and the elderly.
Tips for Faster Recovery
In addition to medical treatment, certain guidelines can help speed up recovery, including:
Getting sufficient rest
Drinking plenty of fluids
Taking medications as prescribed
Avoiding strenuous physical activity during illness
Attending follow-up medical appointments to ensure improvement
The Role of Lifestyle in Reducing Risk
A healthy lifestyle plays an important role in preventing pneumonia and reducing its severity if infection occurs. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamins C and D, helps support the immune system and fight infections. Regular moderate physical activity also improves respiratory efficiency and blood circulation.
Adequate sleep is equally important, as lack of sleep weakens the body’s ability to combat microorganisms. It is also recommended to avoid air pollution as much as possible, whether at work or at home, since inhaling polluted air may irritate the lungs and increase susceptibility to inflammation.
In addition, adherence to healthy daily habits and regular medical check-ups, especially for individuals with chronic diseases, significantly contributes to reducing the risk of pneumonia and improving the chances of rapid recovery if it occurs.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a disease that can be prevented and successfully treated when handled properly. Awareness of symptoms, early diagnosis, and adherence to treatment are essential factors in avoiding complications. Therefore, consulting a physician promptly when experiencing unusual respiratory symptoms is highly recommended to maintain lung health and overall quality of life.