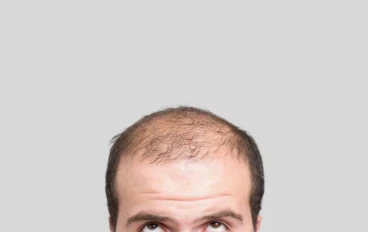
A final solution to the problem of hereditary baldness
Genetic Baldness: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Genetic baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common type of hair loss affecting both men and women worldwide. It primarily results from hereditary factors and the influence of male hormones, particularly the DHT hormone (dihydrotestosterone). Over time, DHT causes hair follicles to shrink, leading to thinner hair and eventually, complete baldness in affected areas.

Causes of Genetic Baldness
1. Genetic Factors:
The main cause of genetic baldness is heredity. People who inherit genes that make their hair follicles sensitive to DHT are more likely to experience gradual hair thinning. This sensitivity causes the follicles to become smaller with each hair growth cycle until they can no longer produce visible hair.
2. Hormonal Influence (DHT):
Testosterone converts into DHT through the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, weakening them and shortening the hair growth phase. Over time, this results in permanent hair loss in specific patterns.
3. Age:
Hair thinning and baldness often become noticeable with age. Men typically start to experience male pattern baldness in their late 20s or early 30s, while women may notice gradual thinning after menopause.
4. Environmental and Lifestyle Factors:
Although genetics play the main role, stress, poor nutrition, smoking, and lack of sleep can accelerate the progression of baldness and weaken the scalp’s health.
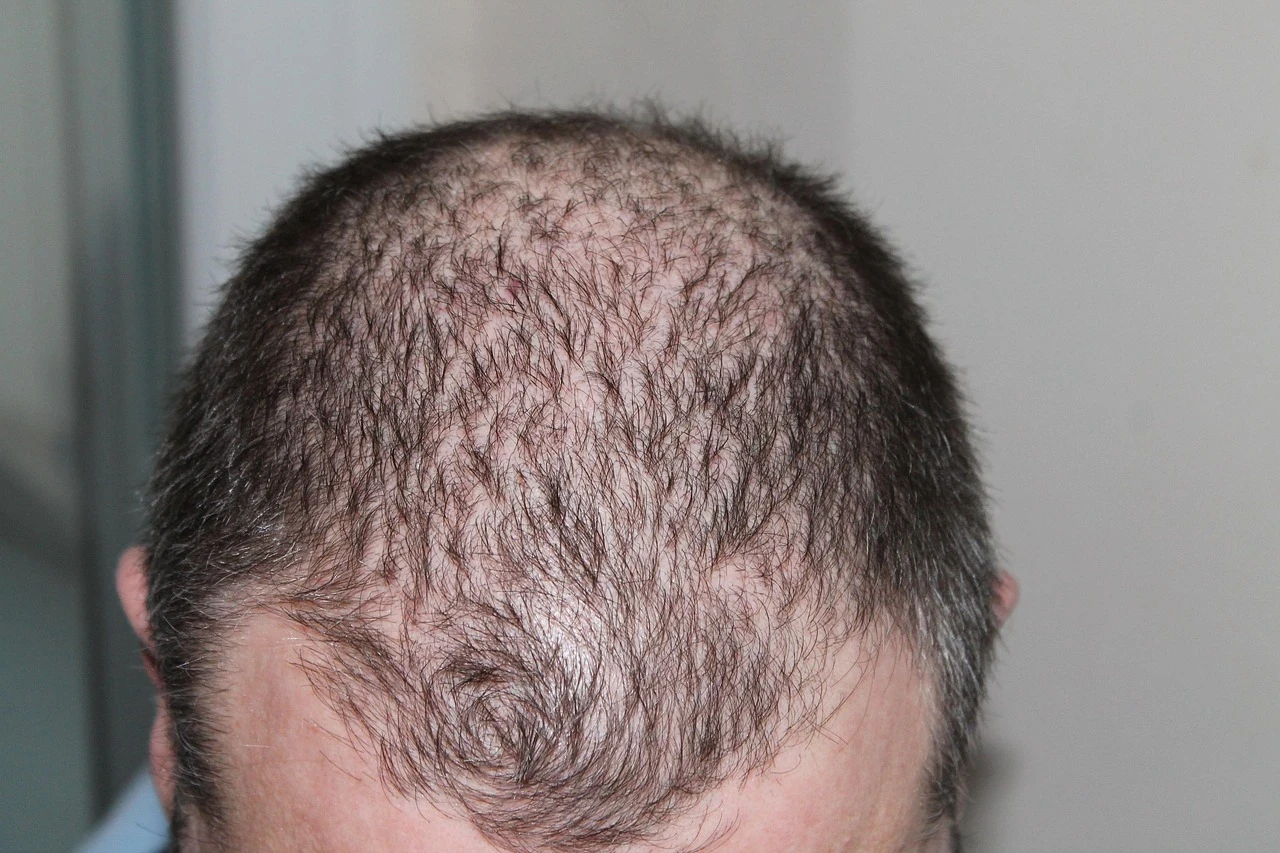
Symptoms and Patterns
In Men:
Hair loss usually begins at the temples or crown of the head, forming an “M” shaped pattern that may progress to complete baldness on the top.
In Women:
Women tend to experience overall thinning at the crown or part line rather than receding hairlines.
Treatment Options for Genetic Baldness
While genetic baldness cannot be completely cured, several medical and cosmetic treatments can slow hair loss and stimulate regrowth:
1. Medications:
Minoxidil: A topical solution applied directly to the scalp to promote hair growth and strengthen follicles. It is approved for both men and women.
Finasteride: An oral medication that reduces DHT production in men, helping to slow or stop further hair loss. It is not recommended for women due to hormonal side effects.
2. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
This treatment involves injecting plasma extracted from the patient’s blood into the scalp. PRP helps stimulate hair follicles and improve scalp circulation, encouraging natural hair growth.
3. Hair Transplant Surgery:
One of the most effective and permanent solutions for baldness. Healthy hair follicles are transplanted from dense areas of the scalp to bald regions, resulting in a natural-looking and lasting effect.
4. Home Care and Prevention:
Maintain a balanced diet rich in protein, iron, and zinc.
Avoid excessive stress and smoking.
Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos.
Massage the scalp regularly to boost blood flow and strengthen follicles.

Preventing Genetic Baldness
Although you can’t change your genes, you can delay or minimize hair loss by adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking medical advice early. Regular scalp care, nutritional supplements, and timely treatments can help preserve your hair density and slow the progression of baldness.
Conclusion
Genetic baldness is a natural and common condition that can affect confidence but is not without solutions. With advances in medicine and cosmetic procedures, people now have many options—from medical treatments to hair transplant surgery—to restore their hair and self-esteem. The key is early intervention, consistent scalp care, and a healthy lifestyle to keep your hair strong and vibrant for as long as possible.