Acne: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention.
Acne: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention.
Keywords
acne, and acne vulgaris clear skin tips ,acne treatment, causes of acne, symptoms of acne, prevention of acne, skin care, skin hormonal
DO you know Acne?

Acne is among the most common skin conditions globally, affecting millions of teenagers and adults worldwide. Whereas many consider acne a trivial skin condition, it is actually a very multifaceted medical condition in itself, involving hair follicles, oil glands, and skin bacteria. Though the manifestations of acne may be no more than a minor nuisance for some, it often impacts self-esteem, emotional well being, and quality of life for others. Overview This article explains the scientific meaning of acne, its symptoms, common causes, methods of treatment, and practical ways of preventing breakouts
Acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris is a chronic skin disorder related to the blockage of hair follicles with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. Each hair follicle has attached Acne sebaceous glands that synthesize oil to lubricate the skin. What is acne? When these glands produce too much oil, pores become blocked, and inflammation with visible acne lesions can occur. Acne typically appears on parts of the body with the greatest number of oil-producing glands, such as:
- Chest
- Shoulders
- Upper back
While acne is most prevalent among teenagers, especially due to hormonal changes, adults may have chronic or new forms of the condition as well.
Types of Acne
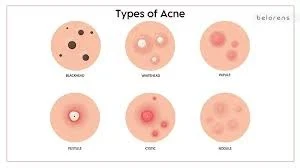
Acne can appear in several different forms, and symptoms vary depending on
the severity of the condition. What is acne? The most common symptoms include:
1. Whiteheads (Closed Comedones)
These occur when oil and dead skin cells block the pore, but the top of the pore closes. The result is a small, flesh colored bump on the skin.
2. Blackheads (Open Comedones)
When a pore does not close, the oil and skin cells trapped inside come into contact with air and darken, causing a black appearance.
3. Papules
Papules are small, red, tender bumps that result from inflammation of hair follicles.
4. Pustules
These are similar to papules but filled with pus, generally red at the base, with a white or yellow top.
5. Nodules
Large, solid, painful lumps beneath the skin that result from deep inflammation.
6. Cysts

Cysts are the severest acne type being painful lumps filled with pus that are deep in the skin and may cause scars if not treated properly.
Besides these physical symptoms, acne can result in emotional consequences such as stress, embarrassment, and loss of self-esteem.
Acne Causes
Acne occurs when a number of factors come together, and each individual may have their combination of causes. The most common ones include:
1. Overproduction of Oil
Overactive sebaceous glands produce too much sebum, increasing the risk of clogged pores.
2. Hormonal Changes
It is during puberty, pregnancy, menstruation, or periods of stress that the levels of one's hormones rise, especially androgens. This then causes the stimulation of oil glands, leading to breakouts.
3. Bacteria
Within these pores, there is an overgrowth of a type of bacteria, Cutibacterium acnes (previously Propionibacterium acnes), that triggers inflammation and infection.
4. Buildup of dead skin cells
Whenever dead cells do not get sloughed off, they mix with oil and block hair follicles.
5. Genetics
If your parents had acne, you are more likely to develop it too.
6. Certain Medications
Drugs containing corticosteroids, testosterone, lithium, or other hormones can cause acne.
7. Diet and Lifestyle Factors
High glycemic foods, sugary snacks, dairy products, and excessive stress can affect the formation of acne in some people.
Acne Treatment
Treating acne requires patience and consistency. Acne treatment should be prescribed based on the type and severity of the condition, but here are some of the most effective and commonly recommended treatments:
1. Topical Treatments
These treatments are applied directly to the skin and are usually the first step in managing acne.
- Benzoyl peroxide: kills acne causing bacteria and reduces inflammation.
- Salicylic Acid: Known to help clog pores by removing dead skin cells.
- Retinoids, such as tretinoin and adapalene facilitate: the turnover of skin cells and prevent the clogging of pores
- Antibiotic cream: reduces bacteria and inflammation.
2. Oral Medications
Doctors may prescribe the following to treat moderate to severe acne:
- Oral antibiotics to reduce bacteria and swelling
- Isotretinoin is a very potent medication used for severe cystic acne not responding to other forms of treatment
- Birth control pills are a kind of hormonal therapy for women with hormonally driven acne.
3. Professional Dermatology Procedures
Dermatologists may also suggest
- Chemical peels
- Laser or light therapy
- Extraction of whiteheads and blackheads
- Steroid injections for painful cysts
These treatments can really help lessen breakouts and improve skin texture.
How to Avoid and Manage Acne?
While acne cannot always be avoided, particularly because of hormonal factors, here are several practical measures that help reduce the risk of breakouts:
1. Keep Your Skin Clean
Wash your face twice a day with a mild cleanser to remove excess oil, sweat, and dirt.
2. Avoid Harsh Scrubbing
Scrubbing irritates the skin, making inflammation worse, and can also spread bacteria.
3. Utilize Non-Comedogenic Products
Use "oil-free" or "non-comedogenic" skin care and makeup products to avoid blocking pores.
4. Do not touch your face.
Touching or picking at acne spreads the bacteria and can result in scarring.
5. Eat Healthy
A diet balanced with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and water can support overall skin health.
6. Manage Stress
Stress increases hormone activity, leading to more breakouts. Relaxation techniques, such as meditation or exercise, can help.
7. Hydrate
Drinking enough water keeps your skin moisturized and promotes the skin's natural healing processes.
Conclusion:
While not an uncommon condition, acne can significantly affect physical appearance and emotional well being. Understanding what acne is, what causes it, and how to manage it is the first step toward clearer and healthier skin. By taking the appropriate skincare steps, getting medical treatments when necessary, and practicing preventive measures habitually, the majority of individuals will be able to considerably reduce acne and improve their confidence. If the acne is severe or will not go away with home remedies, it is best to consult a dermatologist for personalized and effective treatment.
Reference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acne
https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/acne