Omega-3 for Child Development: Building a Smarter, Sharper, and More Focused Brain
Omega-3 for Child Development: Building a Smarter, Sharper, and More Focused Brain

Every parent aspires to provide their child with the best possible foundation for success. We invest in education, enriching activities, and a loving environment. Yet, one of the most powerful tools for unlocking a child's potential may lie in the microscopic architecture of their brain, which is profoundly influenced by a specific group of nutrients: Omega-3 fatty acids. These are not just another health fad; they are fundamental building blocks, literally shaping how a child's brain develops, learns, and behaves. From the rapid brain growth in the womb to the complex neural networking of the teenage years, Omega-3s play a starring role. This article delves into the compelling scientific evidence, explaining precisely how these essential fats enhance cognitive abilities, sharpen focus, and support the behavioral skills every child needs to thrive in and out of the classroom
Understanding Omega-3s: DHA, EPA, and ALA Explained
To grasp their impact, we must first understand what Omega-3s are and why they are deemed "essential
The Key Players: DHA, EPA, and ALA
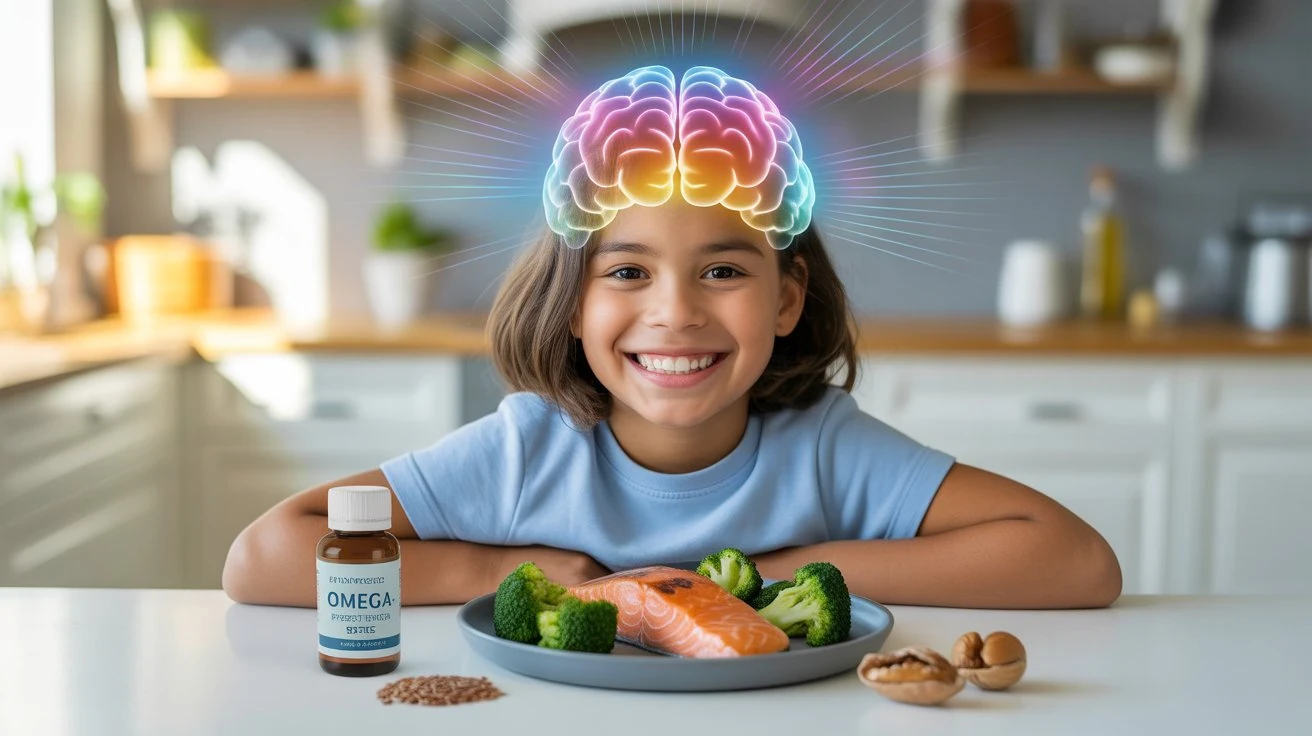
The three most important Omega-3s are ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). ALA, found in plant sources like flaxseeds and walnuts, is a precursor, meaning the body must convert it into the more active EPA and DHA. However, this conversion process in humans is notoriously inefficient. This makes direct sources of EPA and DHA critically important. DHA is the architectural star of the brain, making up over 90% of the omega-3 fats in the brain and is a primary structural component of the cerebral cortex—the area responsible for memory, language, and attention. EPA, while present in smaller quantities, is a powerful modulator of inflammation and blood flow, supporting the overall health and efficient function of the brain's intricate network
Why the Body Can't Do It Alone
Unlike other fats that the body can synthesize, Omega-3 fatty acids are "essential," meaning they must be obtained through diet. During periods of rapid growth—pregnancy, infancy, and childhood—the demand for DHA is exceptionally high. A child's brain undergoes explosive development, creating millions of neural connections every second. DHA is integrated directly into the cell membranes of brain cells, making them more fluid and flexible. This fluidity is crucial for efficient communication between neurons, which is the very basis of all learning, thinking, and skill acquisition
The Scientific Link: How Omega-3s Fuel Cognitive and Behavioral Skills
Decades of research have moved the link between Omega-3s and child development from hypothesis to well-established fact, with benefits spanning multiple domains of skill
Enhancing Cognitive Performance and Academic Learning
Numerous randomized controlled trials, the gold standard in scientific research, have investigated the effects of Omega-3 supplementation on children's cognition. A comprehensive analysis of these studies concluded that supplementation, particularly with DHA and EPA, has a positive effect on aspects of cognitive function. Children showed improvements in measures of memory, the speed at which they processed information, and their ability to learn and retain new vocabulary. These cognitive gains are the direct result of DHA's role in building healthy brain cells and promoting the release of neurotransmitters, the brain's chemical messengers. When brain cells communicate more effectively, learning becomes more efficient
Supporting Focus, Attention, and Emotional Regulation
Perhaps the most widely recognized benefit for school-aged children is Omega-3's impact on attention and behavior. EPA is particularly influential in this domain. Research has shown that Omega-3 supplementation can lead to measurable improvements in attention span, reduced impulsivity, and a decrease in hyperactivity symptoms in children. The mechanisms are multifaceted: EPA helps regulate neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which are critical for mood and focus, and it supports healthy blood flow to the brain. Furthermore, by reducing neuroinflammation, it creates a more stable physiological environment for executive functions to operate. For children struggling with attention challenges, optimizing Omega-3 intake can be a foundational, supportive strategy
Practical Strategies: Ensuring Optimal Omega-3 Intake for Your Child
Knowing the "why" is only half the battle; the "how" is what empowers parents to take action
Dietary Sources: From Sea to Table
The most effective way to increase Omega-3 levels is through diet. The most potent sources of pre-formed DHA and EPA are cold-water fatty fish
Excellent Sources: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and herring.
Good Sources: Tuna (especially light tuna), and to a lesser extent, cod.
Aim to serve these fish 2-3 times per week. For plant-based sources or picky eaters, ALA from chia seeds, ground flaxseed (sprinkled on yogurt or oatmeal), and walnuts can contribute, but remember the conversion to DHA/EPA is limited
Navigating the World of Supplements
For children who refuse to eat fish or have dietary restrictions, high-quality supplements are a practical and effective alternative
Choosing a Supplement: Look for a product specifically formulated for children that provides a balance of both DHA and EPA. The source matters; supplements derived from small fish (like anchovies and sardines) are often purer
Dosage and Safety: A general guideline for children is a combined dose of 500-1000 mg of DHA/EPA daily, but it is always best to consult with your pediatrician for personalized advice. Reputable brands will have third-party testing for purity from heavy metals and other contaminants
Frequently Asked Questions About Omega-3s and Children
At what age should I start giving my child Omega-3s
The need begins in pregnancy, as the fetal brain heavily relies on the mother's DHA intake. For infants, breast milk is an excellent source (assuming the mother consumes enough), and most infant formulas are now fortified with DHA. You can introduce pureed fatty fish when starting solids and consider a liquid supplement after consulting your pediatrician
Can Omega-3s help children with ADHD
Research indicates that many children with ADHD have lower levels of Omega-3 fatty acids. While not a cure or a replacement for prescribed treatments, multiple studies have shown that supplementation can lead to modest but significant improvements in attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity as part of a comprehensive management plan
Are there any side effects to Omega-3 supplements for kids
Omega-3 supplements are generally very safe. The most common side effect is a mild fishy aftertaste or burping. Choosing a high-quality supplement and giving it with a meal can mitigate this. In very high doses, they can have a slight blood-thinning effect, so discussing dosage with a doctor is always prudent
An Investment in Your Child's Neurological Future
Omega-3 fatty acids are far more than just a nutrient; they are a fundamental component of a well-built brain. The evidence is clear: ensuring adequate intake of DHA and EPA is one of the most impactful nutritional steps a parent can take to support their child's cognitive development, academic performance, and behavioral equilibrium. By prioritizing fatty fish or a high-quality supplement, you are not just feeding your child's body; you are directly nourishing the very architecture of their mind, laying the groundwork for a lifetime of learning, focus, and emotional well-being